Gartner Hype Cycles 2016
Die Gartner Hype Cycles spiegeln die Entwicklung der Trends am Markt wieder. Sie gern gesehen bei Anbietern, werden aber leicht belächeltt bei Anwendern. Dennoch sind sie eine gute Grundlage für eine Diskussion der aktuellen Trends.
Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies 2016
Nehmen wir als Einstieg den Gartner "Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies". DIes ist ein Bereichsübergreifender Hype Cycle, der den Fortschritt der wichtigsten zahlreicher Zukunftstechnologien (ein paar Dutzend aus ca. 2000) darstellt und sie auf dem typischen Hype Cycle (mit "Erwartungsberg" und "Enttäuschungssenke") einordnet. Neben der Trenderwartung soll natürlich der Hype Cycle auch Informationen zum Wert und geschäftlichen Nutzen eines Trends aussagen.
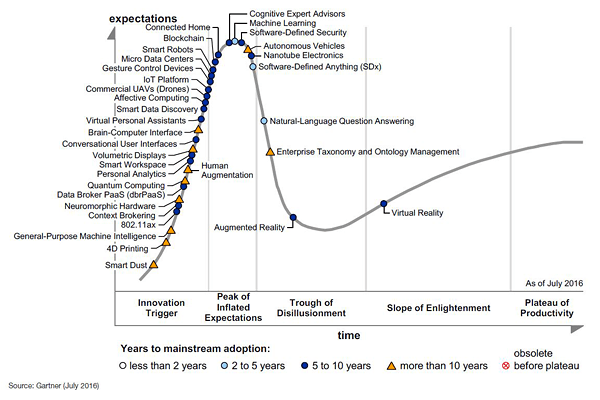
Source: Gartner (August 2016)
Die Kurve zeigt zugleich ein grundsätzliches Problem - es gibt keine linearen, abgegrenzten Entwicklungslinien mehr. Alles ist bei den aktuellen Entwicklungen im technologischen Bereich mit einander verflochten, von einander abhängig, bedingt sich gegenseitig. Damit ergibt sich auch ein Problem für die vielen weiteren, spezialisierten Hype Cycles, die letztlich nur andere Sichten auf die aktuelle laufende Digitale Transformation bieten.
Hype Cycles 2016
So verscuht auch Gartner selbst einen Überblick zu schaffen - mit dem Artikel "Gartner's 2016 Hype Cycles Highlight Digital Business Ecosystems". Hier geht es um vier Megatrends und eine Sammlung aktueller Hype Cycles sowie der Hype Cycles des vorangegangenen Jahres.
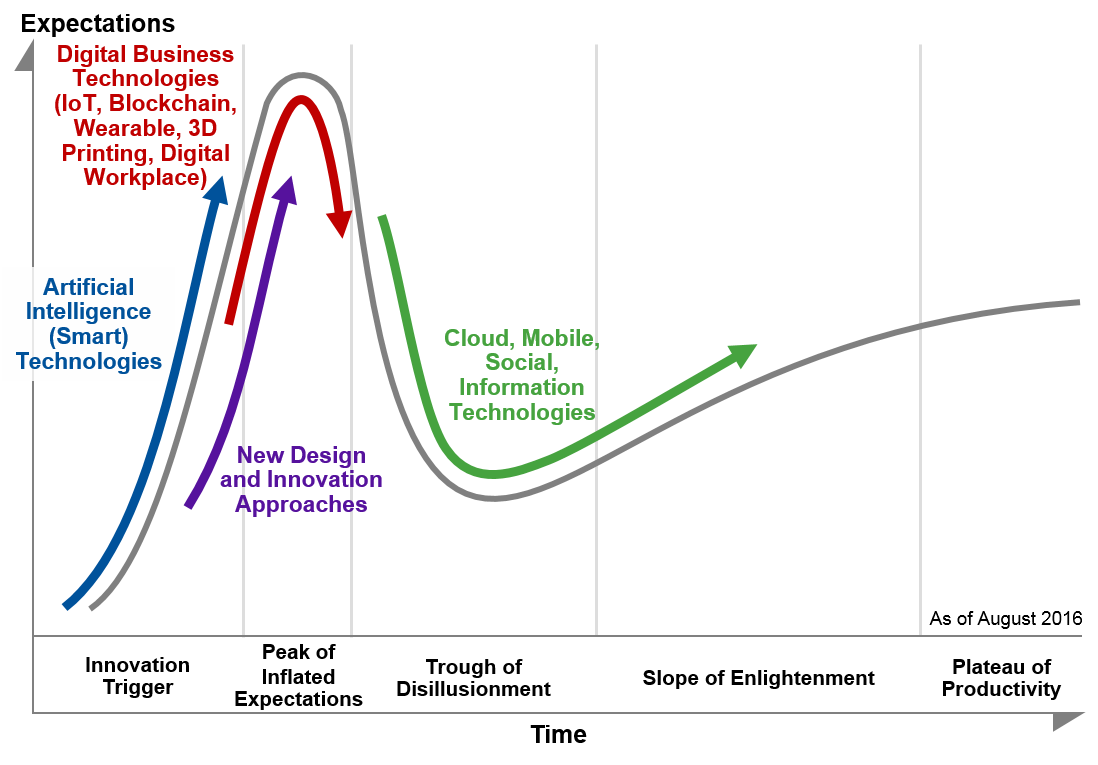
Fig. 1. Megatrends Across Gartner 2016 Hype Cycles. Source: Gartner (August 2016)
Hier werden alle Entwicklungen aus den Dutzenden von Hype Cycles auf vier Mega-Trends heruntergebrochen: Artificial Intelligence, Digital Business mit IoT, New Design and Innovation sowie - bereits auf das Plateau strebend - der SMAC-Stack (Social, Mobile, Analytics, Cloud). Vier grundsätzliche Veränderungen stehen im Fokus:
- Das "Digital Business" tritt in eine neue Ära ein
- Ein neues Zeitalter der Künstlichen Intelligenz und des Maschinenlernens hat begonnen
- Sicherheit und Cloud werden weniger "gehypt", sind aber weiterhin kritisch
- Das Skalierens von Lösungen nach oben wie auch aus den bisherigen Umgebungen heraus wird die nächste Herausforderung
Gartner schreibt in ihrem Bericht dazu <Zitat>:
Today, massively connected ecosystems that include businesses, technologies and people cross geographies, markets and industries. Emerging technologies enable organizations to operate their business ecosystems by:
- Increasing the interconnection of people and things
- Allowing vast quantities of data to be exchanged almost in real time
- Increasing intelligence and allowing complex analysis and decision making in real time
Megatrends Driving Digital Business Evolution
First, we look across all the 109 Hype Cycles to understand the high-level megatrends. With this view, we see that there are several megatrends that track the evolution of digital business technologies, services and business models (see Figure 1).
-
Nexus technologies move to and through the trough:
Since 2008, cloud, data, mobile and social (the Nexus of Forces) have dramatically affected people's lives, business interactions, social change and global economies. These massive collections of technologies and the resulting changes in business models and human behavior have accelerated the interconnection of technology, business and humans, and given rise to digital business. -
Early digital business technologies evolve beyond the hype:
In 2016, the future of business technology has come into sharper focus with the emergence of digital business: the blurring between the digital and physical worlds that is revolutionizing life for people and gives enterprises unprecedented opportunities. While over 90% of large organizations are pursuing digital initiatives, we estimate that fewer than 30% of businesses have fully realized their digital potential at scale (see "Fifty Examples of Digital Business: A CIO and CEO Resource" ). -
New approaches to design and innovation:
Digital business is about more than technologies; it is about creating new business models and new ways to engage with customers, partners and suppliers in your business ecosystem. To drive this innovation, organizations look to strengthen their design and innovation capabilities. Approaches such as human-centric design, design thinking, agile, DevOps, architecting innovation and other iterative, experimental approaches underpin digital business. -
Artificial intelligence adds new dimension to digital business:
The early signs of this evolution are expanding with the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning or smart technologies. Technologies are emerging that can learn and evolve based on information they gather and analyze, and produce unanticipated results. The old automation model moved at the speed of code development; the new model will move at the speed of data. Early versions of this technology are beginning to appear, including smart apps, conversational interfaces, predictive analytics and virtual personal assistants.
The Most Significant Profile Changes Supporting Digital Business
Second, we explored over 2,000 technology, service and discipline profiles to understand those that shifted significantly from 2015 to 2016 to identify common trends and highlight some of the individual technologies, services and disciplines that are having the highest impact.
A Hype Cycle gives a snapshot of how individual technologies, services and disciplines evolve from initial excitement to mainstream tools. It also illustrates how the opportunities for first-mover advantage narrow as innovation progresses. The maturity of technologies accelerates when enterprises find them especially valuable and vendors have invested more to develop them.
Shift No. 1: Digital Business Advances to a New Era
Many enterprises have focused on creating digital versions of analog products and services, or on enhancing conventional products, such as airplanes and locomotives, with sensors. They augmented existing business models, systems, services and technologies. Today, digital business increasingly focuses on new business models based on born-digital products that bridge the digital/physical divide, such as driverless cars and smart utility grids. The largest, most striking group of technologies that are new to our Hype Cycles in 2016 illustrates this trend:
- The Internet of Things (IoT), such as air quality monitors, digital twins and biometric earbuds
- Emerging operational technologies, such as city operation centers and energy-sharing platforms
- Wearable technologies, including personal trackers
- Multidimensional printing, such as 4D printing, 3D-printed drugs and 3D-printed wearables
In addition, a number of first-time technologies and trends offer more general applications in digital business, such as digital ethics and digital experience monitoring. Blockchain represents a whole category in itself, with emerging use cases well beyond traditional financial services — for example, in healthcare and supply chain applications.
Fast-moving technologies on the Hype Cycles reinforce the digital business trend. We looked at technologies that have moved at least five spots along our 60-spot Hype Cycle since 2015. They will contribute to digital business even if they are not strictly digital business technologies:
- Industry-specific technologies or uses, especially in banking (such as open banking), insurance (location intelligence) and healthcare (OpenNotes)
- Mobility (mobile marketing analytics and mobile sports and fitness ecosystems)
- 3D printing, including 3D-printed implants, biotissues and pharmaceuticals
Shift No. 2: A New Age of AI and Deep Machine-Learning Technologies
This year, over 45 technology profiles focus on providing AI, smart or machine-learning capabilities. When organizations think about AI technologies, their minds leap to futuristic robots and systems. The reality is that these technologies are evolving today, and enterprises must begin to figure out the right use cases and when to consider adopting.
- The hype for a vast majority of AI or smart technologies has not peaked.
- The few that have passed the Peak of Inflated Expectations include machine learning, predictive analytics, consumer smart appliances, virtual personal assistants and smart locks, thermostats, fabrics and lighting.
- Industry-specific technologies also appear in several Hype Cycles, including government (smart parking, smart city, smart transportation, and smart city framework), retail (smart data discovery), healthcare (healthcare sages), banking (smart contracts) and education (smart machine education applications).
- Several smart technologies are new this year, including smart contact lenses, badges, rings, automated guided vehicles and footwear.
For most organizations, AI technologies are experimental. However, clients focused on supporting IoT, customer experience and digital business must track these technologies to understand the potential use cases, particularly for their industry (see "Smart Machines Primer for 2016" ).
Shift No. 3: Security and Cloud Are Less Hyped, but Not Less Critical
We continue to see huge client interest in security and cloud via conferences, inquiries, surveys and document reads. However, these technologies are not evolving as quickly as they have in the past:
Security:
Information security threats haven't leveled off. Indeed, digital business only makes them more acute. Nevertheless, CEOs have decided that their enterprises face greater risk from falling behind in digital business than from cyberthreats. CEOs are pushing their organizations to move faster on digital transformation despite the security challenges. The new security profiles that appear on this year's Hype Cycle, such as blockchain for data security, digital security and crowdsourced security testing platforms, relate to digital business and other trends mentioned above.
Cloud:
Of the over 75 profiles for cloud technologies, services and disciplines, the overwhelming majority have moved beyond the peak. In fact, cloud computing has evolved to the point that it is considered to be a mainstay in the IT portfolio.
The lessening of market hype doesn't mean that either security or cloud is less important. Clients must pay attention to these technologies because digital business is unachievable without them.
Shift No. 4: Scaling Up and Out Becomes the Next Challenge
For 10 years, enterprises have been industrializing their technology, that is, creating robust systems that run at the enterprise level or beyond and can be quickly scaled up to handle new business demands. Digital business and broader business ecosystems have accelerated this trend. Many companies have created viable digital businesses, and leaders now seek to scale them up so that they contribute materially to financial results. Digital business will also accelerate the trend of extending operations beyond enterprise boundaries to support partnerships with people and other enterprises. A large number of technologies that support this trend have appeared on Gartner Hype Cycles for the first time:
- Flexibility and scale: Especially cloud and platform-as-a-service technologies
- Optimization: Emergent changes to established strategies (such as Flip ERP and unified endpoint management to manage all devices in the organization)
- Analytics and algorithms: Technologies that enable enterprises to gain more insight and to automate decisions and actions (deep reinforcement learning, algorithmic business, algorithmic IT operations platforms)
Many fast-moving technologies contribute to this trend as well:
- In-memory computing: Such as in-memory-computing-enabled packaged supply chain planning applications and in-memory data grids.
- Cloud and mobile: At least 10 in each category are fast movers (cloud migration tools, mobile back-end services).
- "Breadth": Technologies that advance integration or otherwise extend the reach of enterprise systems, including technologies labeled "enterprise" (enterprise workforce management), "integrated" (integrated backup appliances), "open" (open APIs) and "inter-" (intercompany multimodal federation).
</Zitat>
Ein Überblick über alle Gartner Hype Cycle
Sehr nützlich ist der Überblick über die wichtigsten Garter Hype Cycle - Gartner nennt sie selbst die "populärsten Hype Cycle". Letztlich sind es nur unterschiedliche thematische Sichten. Den weit über 100 Hype Cycles liegen über 2000 technische Profile zugrunde. Gartner bietet als Service an, die Hype Cycle speziell auf Regionen, Branchen oder spezifische Anforderungen zuzuschneiden.
Populär
Übersicht der diesjährigen Version derjenigen Hype Cycle, die in 2015 die meiste Resonanz bei Gartner-Kunden fanden:
"Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Cloud Computing, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for the Internet of Things, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Data Science, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Business Intelligence and Analytics, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Cloud Security, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Information Infrastructure, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Identity and Access Management Technologies, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Storage Technologies, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Enterprise Architecture, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Smart Machines, 2016"
Veränderungen
Neue bzw. neu definiert wurden folgende Hype Cycle:
"Hype Cycle for Blockchain Technologies and the Programmable Economy, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Information Governance and Master Data Management, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for IoT Standards and Protocols, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Wearable Devices, 2016"
Spezielle Hype Cycle für bestimmte Zielgruppen
CIOs
"Hype Cycle for Blockchain Technologies and the Programmable Economy, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies, 2016"
Enterprise Architecture and Technology Innovation
"Hype Cycle for Enterprise Architecture, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Application Architecture, 2016"
Data and Analytics
"Hype Cycle for Enterprise Information Management, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Business Intelligence and Analytics, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Information Infrastructure, 2016"
Applications
"Hype Cycle for Application Services, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Application Development, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Postmodern ERP, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Business Intelligence and Analytics, 2016"
Infrastructure and Operations
"Hype Cycle for I&O Automation, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Cloud Computing, 2016"
Program and Portfolio Management
"Hype Cycle for Project and Portfolio Management, 2016"
Security and Risk Management
"Hype Cycle for Identity and Access Management Technologies, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Cloud Security, 2016"
Sourcing and Vendor Relationships
"Hype Cycle for Procurement and Sourcing Solutions, 2016"
Supply Chain Leaders
"Hype Cycle for Supply Chain Execution Technologies, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Chief Supply Chain Officers, 2016"
Marketing Leaders
"Hype Cycle for Digital Marketing and Advertising, 2016"
Technology and Service Providers
"Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for the Internet of Things, 2016"
"Hype Cycle for Business Intelligence and Analytics, 2016"
Weitere Gartner-Ressourcen zum Thema
Nicht alle diese Ressourcen können kostenfrei heruntergeladen werden :(.
Analyst Webinar: "Gartner Hype Cycles 2016: Major Trends and Emerging Technologies"
Erläuterung zur Systematik: "Understanding Gartner's Hype Cycles"
Zum Vergleich die Mega Tredns aus 2015: "Gartner's Hype Cycles for 2015: Five Megatrends Shift the Computing Landscape"
Zuletzt aktualisiert am 28.08.2016. Autorenrechte.
Persistente URL: http://www.pc.qumram-demo.ch/ecm/in_der_diskussion/gartner_hype_cycles_2016

Kommentare
Zugang zu Informationen
Wie schon geschieben, koennen diese Informationen nicht durch jedermann gelesen werden. Daher danke fuer das Zitat.
Es zeigt das Gartner gute Dinge schreibt, bestimmt auch entsprechende Kosten macht und dafuer einen ROI haben will. Leider bleibt hiedurch die Mauer fuer viele interssierte stehen.
Mfg.
P Hulsebosch
Kommentar hinzufügen